
Blue Light and Health: Quantum Biology Reveals Hidden Threats of Modern Lifestyle
In today's digital world, where computer screens, phones, tablets, and LED lighting are everywhere, we spend increasing amounts of time exposed to blue light. This seemingly harmless aspect of modern life, however, hides significant health risks that have only recently been uncovered by quantum biology, a groundbreaking field that combines insights from quantum physics with biological systems.
Retina as the Body's Main Regulator
The retina is not only an organ of vision but also plays a crucial role as the entry point for light that influences our biological rhythms. Specific receptors in the retina, primarily melanopsin, detect blue light and send signals to the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) in the hypothalamus. The SCN controls our circadian rhythms, which are internal biological clocks affecting hormone secretion, sleep, metabolism, immunity, and even mood.
Next to the SCN, there is also the habenular nucleus, a brain structure that plays a crucial role in mental health, emotion regulation, and stress response. Disruption of retinal function by blue light therefore affects not only physical health but also significantly impacts mental well-being, causing anxiety, depression, and chronic fatigue.
The groundbreaking study by the Di Meo et al. team (2025)
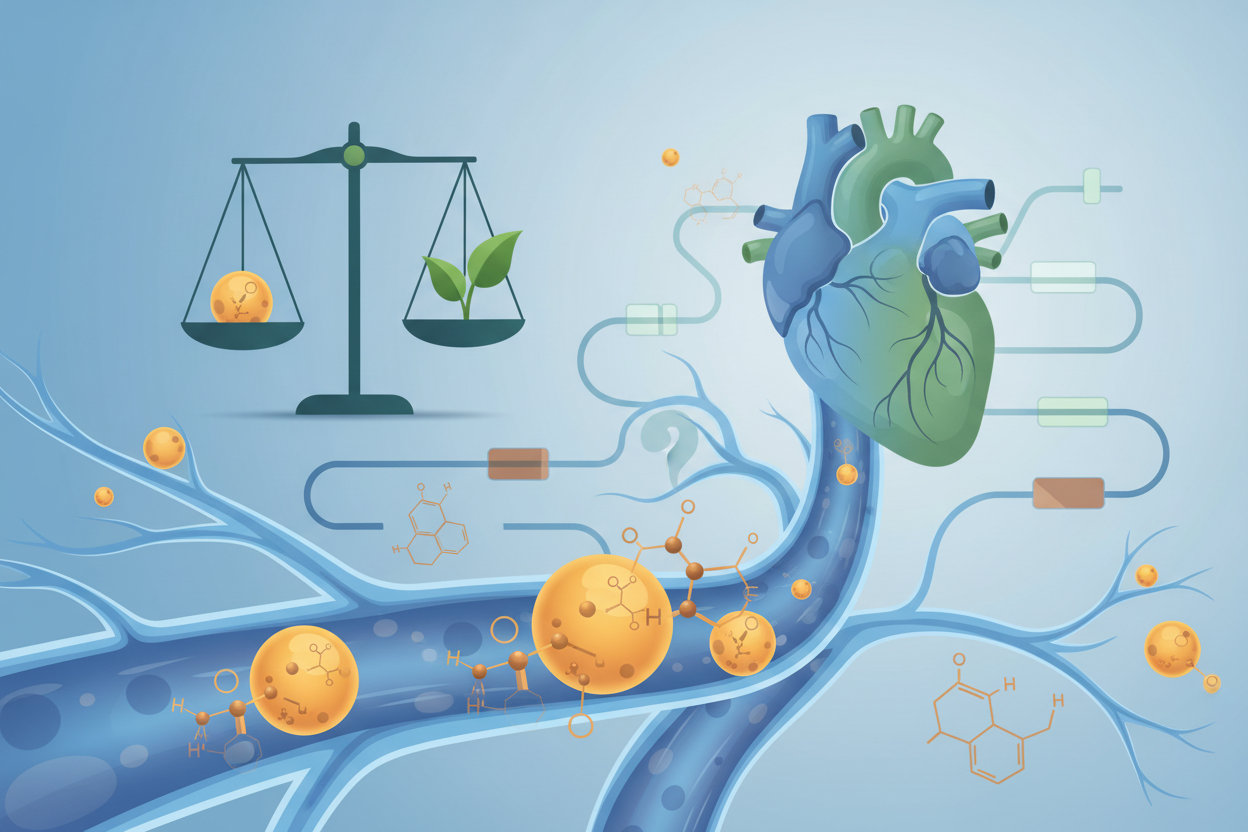
A study by the team of Di Meo et al. (2025) provided key insights into the effects of blue light on the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which is essential for maintaining cellular balance, immunity, metabolism, pain regulation, and neuroprotection. The ECS consists of CB1 and CB2 receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids that the body naturally produces. The study's findings were dramatic:
• ECS receptors (CB1 and CB2) were increased by 250% under blue light.
• Expression of the PPARγ receptor, an important regulator of inflammatory processes, was also increased.
• The level of the enzyme NAPE-PLD, which is responsible for producing protective endocannabinoids, decreased by 40%.
The consequences of these changes are serious. Disruption of the ECS leads to chronic inflammation, cell degeneration, and an increased risk of developing systemic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, neurological disorders, chronic pain, and even certain forms of cancer.
Mitochondria, Pseudohypoxia, and Obesity
Another key role in the negative effects of blue light is played by mitochondria, the organelles responsible for cellular energy production. Blue light causes mitochondrial dysfunction indirectly – it leads to pseudohypoxia, a condition where cells have enough oxygen but cannot use it effectively. This condition arises mainly from a change in the oxidation state of iron (Fe2+ to Fe3+), which significantly disrupts energy (ATP) production and increases oxidative stress in the cells.
Pseudohypoxia then blocks effective fat burning and causes fat accumulation, which directly promotes the development of obesity and insulin resistance. Over the long term, this disruption of metabolic processes can lead to type 2 diabetes and other metabolic diseases.
Chronic Diseases and Oncology
Blue light is now considered part of a broader cascade of causes behind many modern chronic diseases. In addition to the already mentioned obesity and diabetes, disruption of cellular processes and increased inflammation can also contribute to the development of neurodegenerative diseases, heart conditions, autoimmune disorders, and even cancer. Cancer has become increasingly common in recent years, and new data suggest that chronic inflammation and disturbances in cellular energy metabolism—also caused by exposure to blue light—may be significant factors in its development.
Mental Health and Circadian Disruption
Disruption of natural biological rhythms caused by blue light has serious impacts on mental health. Chronic insomnia, anxiety, depression, and reduced psychological resilience to stress – all of these can result from the disruption of SCN and habenular nucleus regulation.
Practical protection and prevention
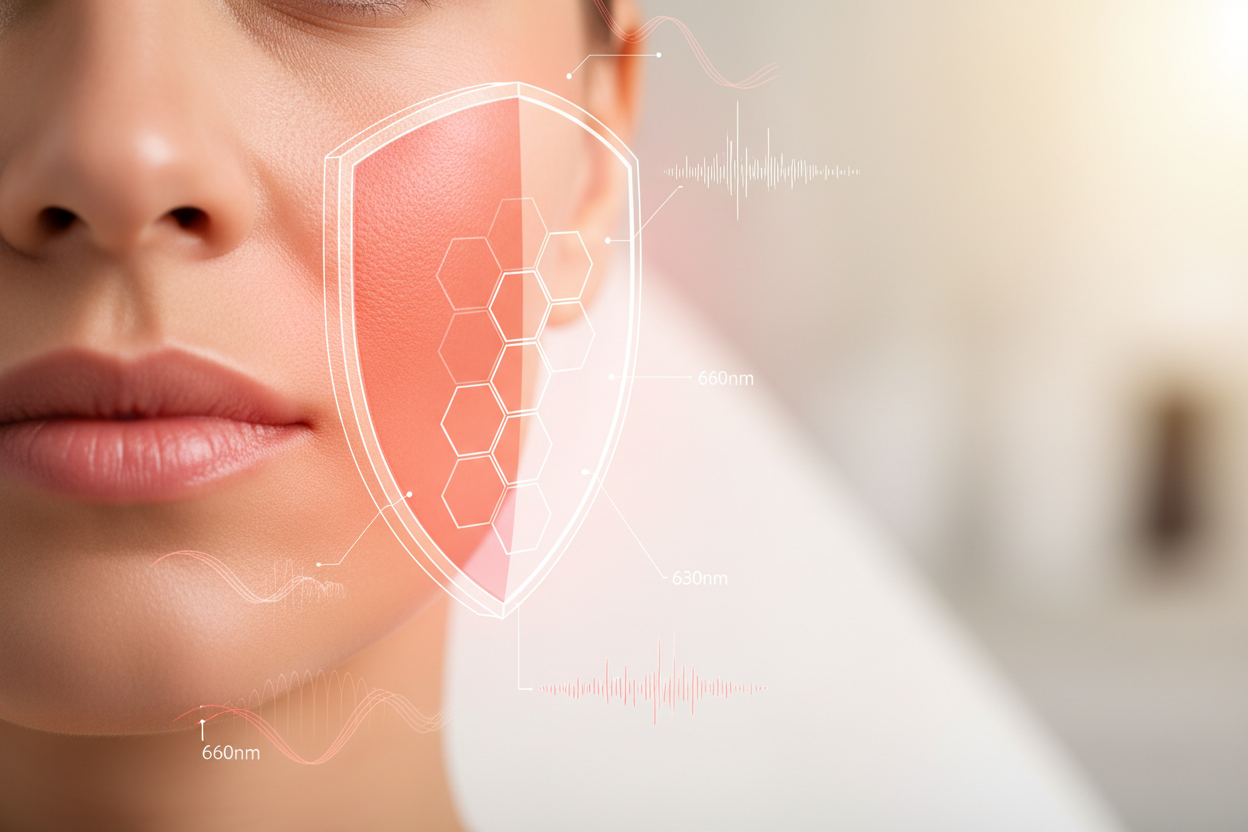
The key to prevention is limiting exposure to blue light. Protection includes special glasses with blue light filters, screen filters, and photobiomodulation panels, such as those from redlight.doctor, which use precisely defined light wavelengths to support cell regeneration, restore ECS balance, and mitochondrial functions.
A Challenge for Medicine and Individuals
Modern medicine should now understand health in a broader context of physical and biological factors. Quantum biology provides us with a new framework for understanding the deep causes of chronic diseases. Each of us has the opportunity to contribute to the prevention of these diseases through a conscious approach to technology and the light that surrounds us. Health is largely in our own hands, and how we use this knowledge is our choice.
Details of the study by Di Meo et al. (2025) can be found here: Di Meo et al., 2025.

Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.