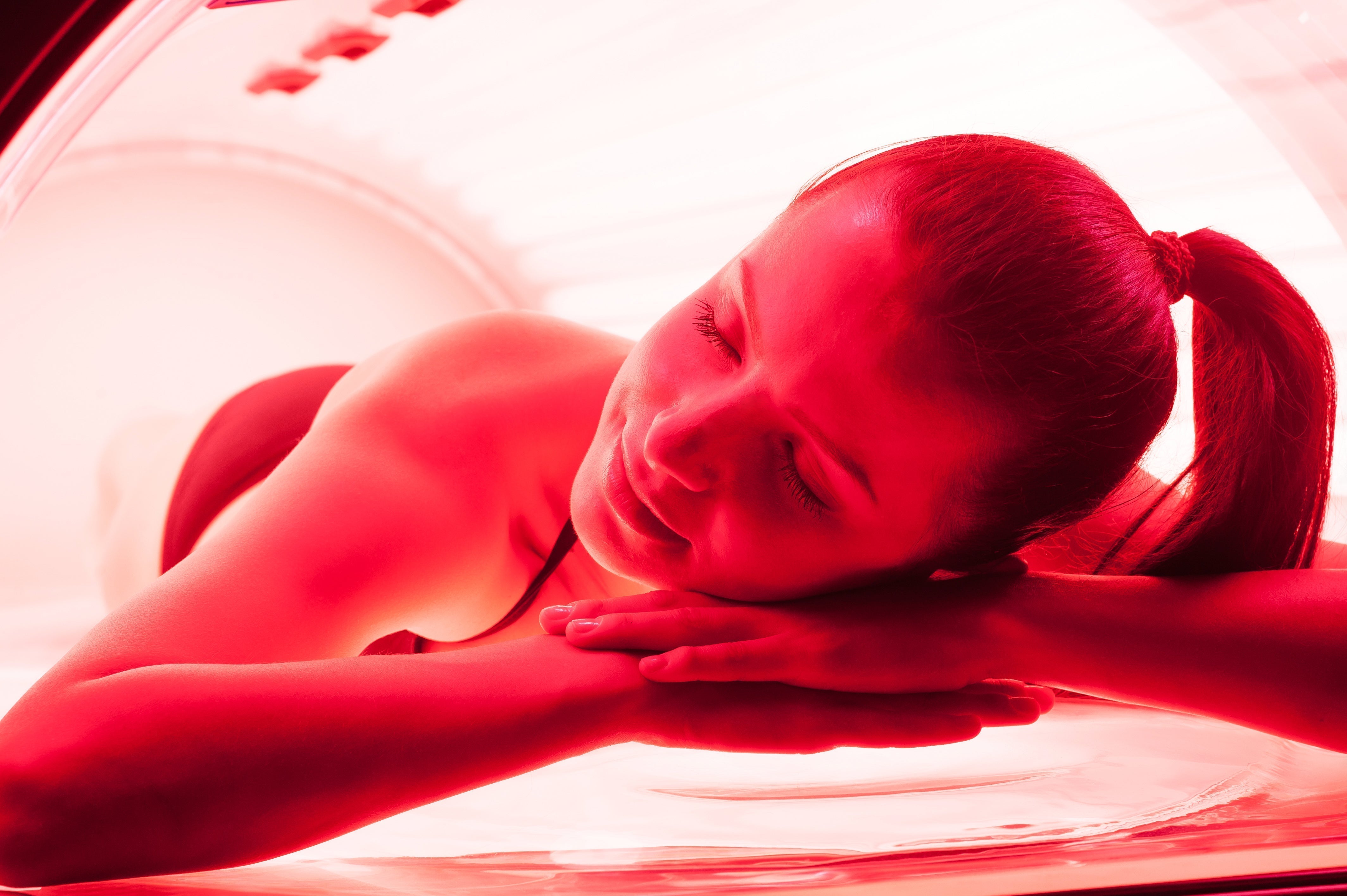

Photobiomodulation and antioxidants: A new approach to treatment with cell therapy
Specific motivation
Scientists are looking for effective ways to regulate oxidative stress (OS) in split or transplanted cells or tissues. Among the promising ideas are photobiomodulation (PBM) and antioxidant therapy, which could protect cells from damage and increase the efficiency of cell therapy .
🔍 What the study confirms
-
Antioxidants: mixtures of molecules with a reducing effect that decrease ROS (reactive oxygen species) and help prevent cellular dysfunction.
-
Photobiomodulation (PBM): the application of low-energy light (e.g., red or NIR) activates mitochondria, improves cellular respiration and signaling, all without harmful side effects.
Combined benefits
-
Synergistic effect: antioxidants remove existing stress, PBM activates mitochondrial functions and supports cellular regeneration.
-
Potential for use in transplants, tissue grafts, or regenerative medicine, where cell survival is crucial.
Where to next?
-
Clinical studies – to demonstrate efficacy in human tissues.
-
Optimal dosage – choose the correct source and dose of PBM, as well as the type of antioxidants.
-
Safety and long-term effect – minimize side effects during therapeutic application.
In conclusion
This article confirms that photobiomodulation together with strong antioxidant therapy forms a powerful tool to increase cell resistance to oxidative stress, especially in the context of cell therapies. It is a promising step towards more effective regeneration and transplantation.
link to the study: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7177783/


Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.